Disclosure: This post may contain affiliate links, meaning we get a commission if you decide to make a purchase through our links, at no cost to you. See our full disclosure here.
Horticultural oil is a time-tested and environmentally conscious solution for managing various pests and diseases afflicting plants. For many decades, it has been a staple tool for gardeners, farmers, and landscapers who seek to safeguard the health and vitality of their plants while minimizing harm to the surrounding ecosystem. This comprehensive exploration delves into the intricacies of horticultural oil, examining its composition, optimal timing for application, methods of use, and best practices to ensure its effectiveness.
What Exactly IS Horticultural Oil Spray?
At its core, horticultural oil is a refined product derived from either petroleum or plant-based sources, meticulously planned for plant pest control. Its primary mode of action involves the suffocation of insects and their eggs or the disruption of their feeding behaviors, ultimately leading to their demise. The application of horticultural oil is typically achieved through spraying, directly targeting the foliage of plants where pests such as aphids, scale insects, mites, and whiteflies tend to congregate. Beyond its insecticidal properties, horticultural oils also play a role in disease management by hindering the spread of fungal spores, thus contributing to the plant’s overall health. The oil leaves behind a delicate coating on the plant’s surface upon application. This coating acts as a physical barrier, effectively preventing pests from engaging in essential life processes like respiration and egg-laying, thereby providing robust control over infestations. Ultimately, it’s like a bodyguard for your plants!

Varieties of Horticultural Oils
Horticultural oils are broadly classified into two main categories, each with its own specific characteristics and applications.
- Petroleum-based oils: These oils, derived from minerals or petroleum, represent the most commonly used and highly effective horticultural oil. Their widespread use is attributed to their relatively low cost and efficacy in controlling a broad spectrum of pests. The refining process for these oils has evolved significantly over the years, resulting in products that are safer for plants and more effective against pests.
- Vegetable-based oils: As the name suggests, these oils are derived from plant sources, such as soybean or cottonseed. They appeal to organic gardeners who prioritize natural and sustainable gardening practices. Vegetable-based oils are often labeled organic horticultural oils, reflecting their plant-derived origin and suitability for organic gardening systems.
Optimal Timing for Horticultural Oil Application
The effectiveness of horticultural oil is heavily influenced by the timing of its application. Applying it appropriately is crucial for achieving optimal pest and disease control. At the same time, incorrect timing can diminish its efficacy or even cause harm to the plants. There are three primary scenarios when horticultural oil can be effectively utilized: during the dormant season, during the growing season, and as a preventative measure.
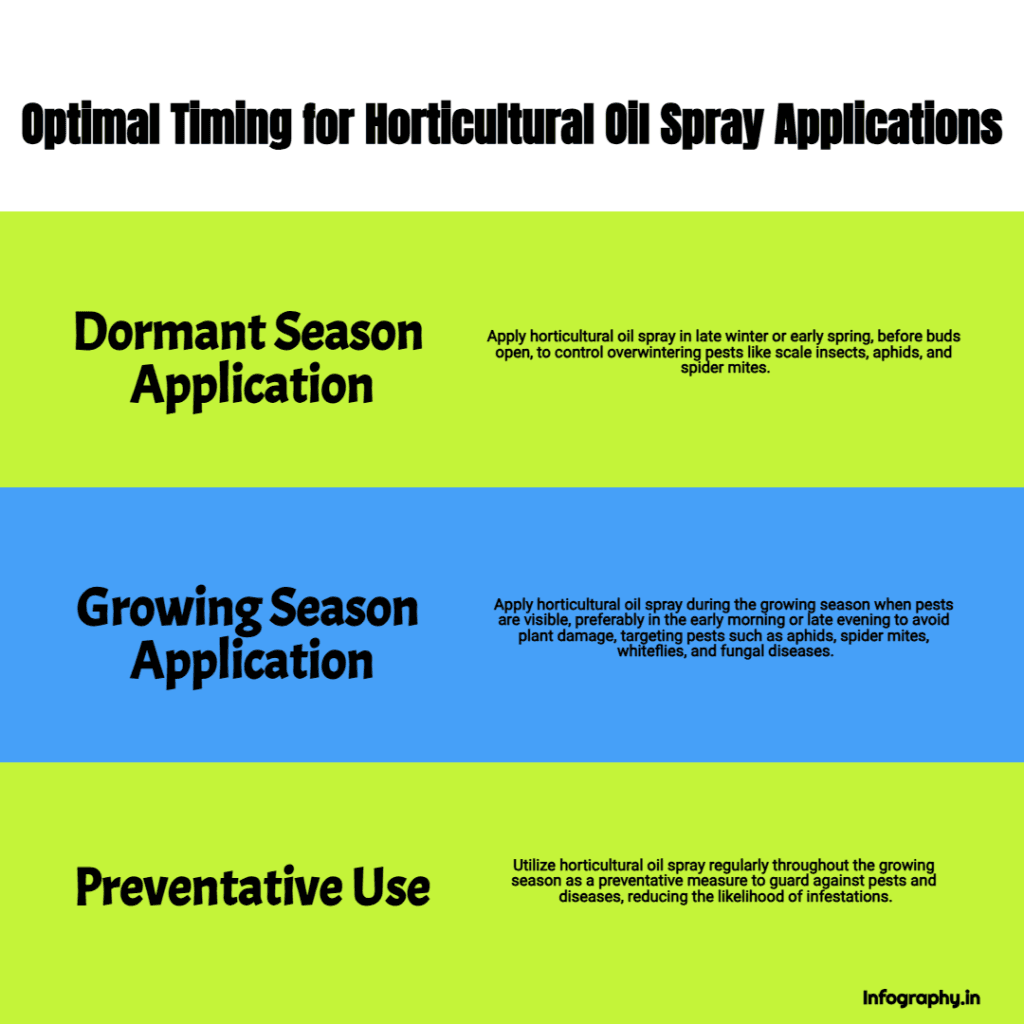
Dormant Season Application
Applying horticultural oil during the dormant season, often called dormant oil application, is a strategic approach to controlling overwintering pests.
- Timing: The ideal time for dormant oil application is late winter or early spring. It is essential to apply the oil before the buds of the plants begin to break but after the risk of freezing temperatures has passed. This timing ensures that the oil targets the pests while still in their dormant, overwintering stage, making them more vulnerable.
- Purpose: The primary purpose of dormant oil application is to control pests that overwinter on trees and shrubs, such as scale insects, aphids, and spider mites. These pests often hide in crevices and under bark during winter, making them difficult to reach with other control methods.
- Effectiveness: Dormant oil applications are highly effective because they directly target the insects in their overwintering stage, significantly reducing the likelihood of infestations during the spring and summer growing seasons. By eliminating the pests before they become active, dormant oil treatments can prevent significant damage to plants later in the year.
Growing Season Application
Horticultural oil can also be applied during the growing season to control active pests.
- Timing: During the growing season, horticultural oil can be applied whenever pests are on the plants. However, using it in the early morning or late evening is generally best. This timing avoids the heat of the day, which can increase the risk of plant damage from the oil.
- Purpose: The purpose of growing season applications is to control active pests feeding on or damaging plants. Common target pests include aphids, spider mites, whiteflies, and fungal diseases like powdery mildew.
- Effectiveness: Horticultural oil works by smothering insects on contact, making it an effective way to quickly reduce pest populations. However, growing-season applications may need to be repeated to achieve complete control, as the oil only kills the pests present at the time of application.
Preventative Use
Horticultural oil spray can be used preventatively to protect plants from pest infestations and diseases in addition to dormant and growing season applications.
- Timing: Horticultural oil can be applied regularly throughout the growing season for preventative use. The frequency of application will depend on the specific pests and diseases prevalent in the area and the susceptibility of the plants being treated.
- Purpose: Preventative applications aim to prevent pests from establishing colonies or spreading diseases to plants. By creating a barrier against pests and pathogens, horticultural oil can help to maintain plant health and vigor.
- Effectiveness: While preventative applications may not provide immediate pest control, they can effectively reduce the long-term incidence of pest and disease problems. Regular preventative treatments can help keep pest populations at low levels, making plants less likely to experience severe infestations.
Proper Application Techniques for Horticultural Oil
To maximize horticultural oil’s effectiveness and minimize plant damage risk, it is essential to follow correct application techniques. Several key factors contribute to a successful application, including choosing the right weather conditions, preparing the solution properly, applying the oil evenly, and reapplying as needed.
Selecting Appropriate Weather Conditions
The weather conditions at the time of application can significantly impact the effectiveness and safety of horticultural oil treatments.
- Temperature: It is crucial to apply horticultural oil when temperatures are between 40°F and 85°F. Applying the oil in extreme heat or cold can increase the risk of plant damage. High temperatures can cause the oil to evaporate too quickly, reducing effectiveness. At the same time, freezing temperatures can prevent the oil from spreading correctly and may also harm plants.
- Humidity: High humidity levels can also interfere with the effectiveness of horticultural oil. It is best to avoid application when humidity is high or when rain is expected within 24 hours. High humidity can slow the drying of the oil, increasing the risk of plant damage and reducing its ability to effectively suffocate pests. Rain can wash the oil off the plants before it has had a chance to work.
- Wind: Wind can also be a significant factor in the success of horticultural oil applications. It is important to apply the oil during calm conditions to prevent drift. Wind can carry the oil away from the target plants, reducing its effectiveness and potentially damaging non-target plants.
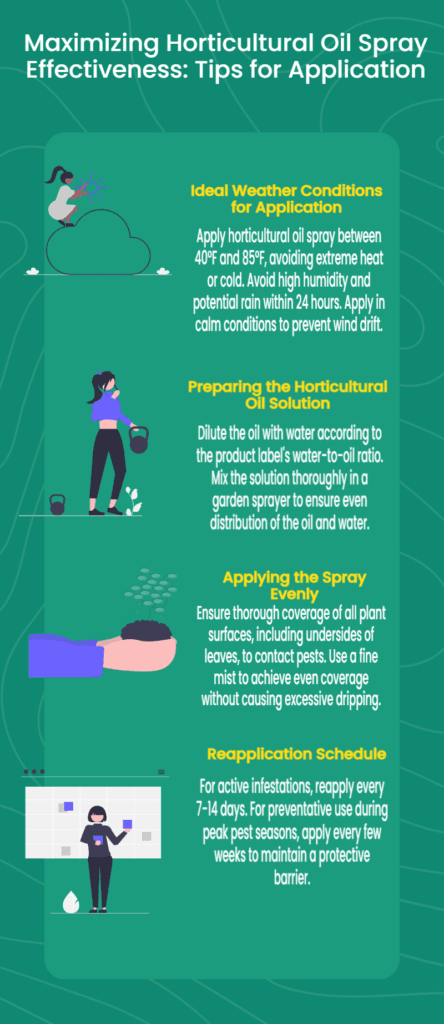
Preparing the Horticultural Oil Solution
Proper preparation of the horticultural oil solution is essential to ensure its effectiveness and safety for use on plants.
- Dilution: The most critical aspect of solution preparation is to follow the product label for the correct water-to-oil ratio. Horticultural oils are typically concentrated and must be diluted with water before application. The proper dilution ratio will vary depending on the specific product and the intended use (dormant or growing season application). Using too much oil can damage plants, and using too little will reduce its effectiveness.
- Mixing: Once the correct amount of oil has been measured, it should be added to a garden sprayer. The sprayer should then be shaken well to ensure an even mixture of oil and water. Proper mixing is essential to ensure the oil is evenly distributed and the spray effective.
Applying Horticultural Oil Evenly
To achieve optimal pest control, applying horticultural oil evenly to all plant surfaces is essential.
- Coverage: When spraying, it is essential to thoroughly cover all plant surfaces, including the undersides of leaves where pests often hide. Complete coverage is necessary to maximize contact with the pests and ensure they are effectively suffocated.
- Avoiding Excessive Dripping: While thorough coverage is important, excessive dripping is also necessary. Dripping can lead to runoff, reducing the effectiveness of the treatment and potentially damaging the plant. Apply the oil in a fine mist to ensure even coverage without oversaturation.
Reapplying Horticultural Oil as Needed
The need for reapplication will depend on the specific circumstances, such as the severity of the infestation and whether the application is for active control or preventative purposes.
- Active Infestations: For active pest infestations, it is typically necessary to reapply horticultural oil every 7-14 days until the pests are effectively controlled. This repeated application ensures that new pests that hatch or emerge after the initial treatment are also eliminated.
- Preventative Use: Horticultural oil spray can be applied every few weeks during peak pest seasons to prevent pests and diseases. Regular preventative applications help maintain a protective barrier against pests and diseases, reducing the likelihood of infestations and outbreaks.
Safety First: Guidelines and Precautions
While horticultural oil is generally considered safe for use around plants and the environment, certain safety guidelines should be followed and precautions taken to minimize any potential risks.
Testing Before Full Application
Before applying horticultural oil to an entire plant, it is advisable to test it on a small, inconspicuous portion. After testing, wait 24-48 hours to observe for any adverse effects, such as leaf burn or discoloration. This precautionary step helps to identify any potential sensitivity of the plant to the oil and prevents widespread damage.
Avoiding Sensitive Plants
Certain plants are known to be sensitive to horticultural oil, particularly during specific stages of growth. It is essential to avoid spraying oil on these sensitive plants, which include:
- Ferns
- Blue spruce
- Japanese maples
- Certain flowers, such as impatiens and fuchsia
Protecting Beneficial Insects
Although horticultural oil is generally safe for the environment, it can still pose a risk to beneficial insects, such as bees, if misapplied. To minimize harm to beneficial insects, it is best to apply horticultural oil early in the morning or late in the evening when bees are less active. This timing reduces the likelihood of direct contact between the oil and the pollinators.
Proper Storage
Proper storage of horticultural oil is essential to maintaining its effectiveness and preventing accidents. It should be stored in a cool, dry place, away from direct sunlight and heat. It is also crucial to keep it out of the reach of children and pets to prevent accidental ingestion or contact.
Advantages of Using Horticultural Oil Spray
Horticultural oil offers several notable benefits, making it a valuable tool for plant care and maintenance.
Environmental Friendliness
One key advantage of horticultural oil is its minimal impact on the environment when used correctly. Horticultural oils degrade quickly and do not leave harmful residues in the soil or water, making them a more environmentally responsible choice compared to some synthetic pesticides.
Effective Pest Control
Horticultural oil is highly effective in controlling many common plant pests. It targets soft-bodied insects, including aphids, mites, whiteflies, scale insects, and mealybugs. It provides comprehensive control over many of the most prevalent garden pests.
Disease Prevention
Horticultural oil can control pests and prevent certain plant diseases. Reducing the spread of fungal spores can help prevent diseases such as powdery mildew and rust. This dual action against pests and diseases contributes to plants’ overall health and resilience.
Safety for Edible Plants
When used as directed, horticultural oils are generally safe for use on fruit trees, vegetable gardens, and ornamental plants. This makes them a suitable option for gardeners concerned about using potentially harmful chemicals on plants they intend to eat.
Troubleshooting Common Problems
Despite its effectiveness and safety, some common issues may arise when using horticultural oil. Understanding these potential problems and their solutions can help gardeners avoid them and ensure successful pest and disease control.
Oil Burn on Leaves
One common problem is oil burn on leaves, which can occur when horticultural oil is applied during high heat or in direct sunlight. To prevent oil burn, it is essential to always apply horticultural oil during the cooler parts of the day, such as early morning or late evening, or when the plants are shaded.
Poor Pest Control
Poor pest control can result from inadequate plant coverage or a diluted solution. To ensure effective pest control, it is crucial to provide complete coverage of all plant surfaces, including the undersides of leaves, and to follow the correct dilution ratios specified on the product label.
Damage to Beneficial Insects
If horticultural oil is applied when beneficial insects, such as pollinators, are active, damage can occur. To minimize harm to beneficial insects, spraying horticultural oil early in the morning or late in the evening when pollinators are less active is best.
Conclusion
If you’re feeling like horticultural oil could be a good addition to your garden arsenal, here’s one we’ve used and liked!
- INSECT KILLER – this pest control is great for use on aphids, leaf miners, leafhoppers, trips, spider mites, scales, whi…
- FOLIAGE PROTECTOR – our insecticide is designed for use on a variety of trees & plants including corn, Potatoes, Apples,…
- DORMANT & GROWING SEASON SPRAY – this product is designed for safe use during both the dormant and growing season. Appli…
Horticultural oil is a versatile and valuable tool for managing pests and plant diseases while minimizing environmental impact. Gardeners can cultivate healthier and more productive gardens by understanding when, how, and where to use them effectively. It is always essential to adhere to product instructions, practice safe application techniques, and closely monitor plant response to ensure the best possible results. With proper and consistent use, horticultural oil can become indispensable to any integrated pest management strategy, promoting sustainable and thriving gardens.
Disclaimer: This post is for informational purposes only and should not be construed as health, wellness or nutrition advice. Please see our full disclaimers here.



Leave a Reply